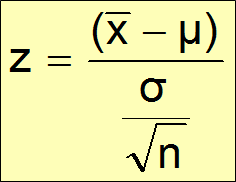Sampling Distribution with Central Limit Theorem and z-value
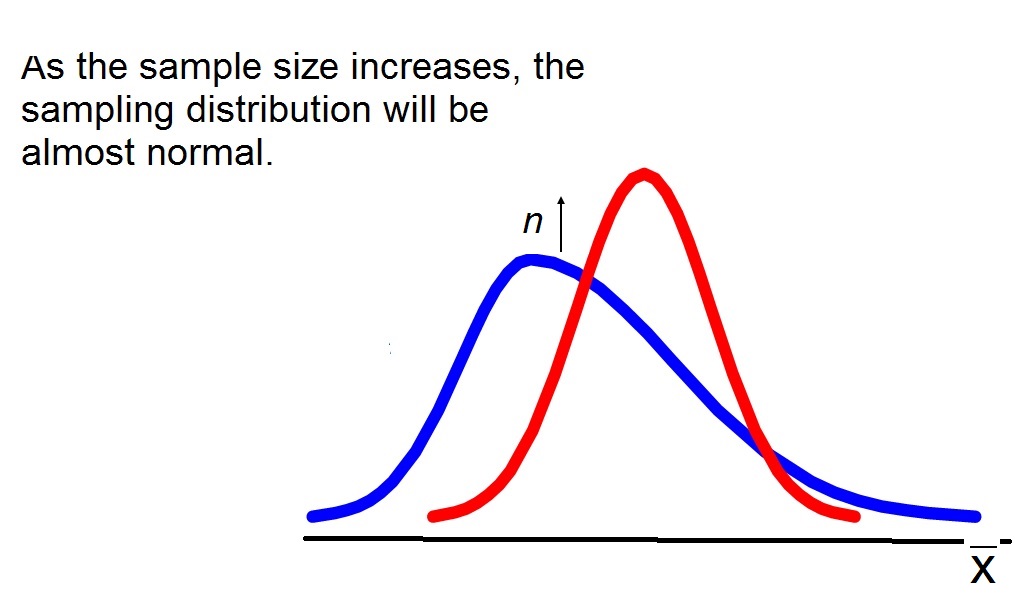
Central Limit Theorem
If the population is normally distributes then the Central Limit Theorem (CLT)is applied. However,
if the population is not normally distributed normal and the sample size is large enough (greater than 30),
it is possible to apply the CLT:
In this case, the sample means from the population will be approximately normal and the sampling distribution will have the properties:
z-value for Sampling Distribution of X̄
Z-value for the sampling distribution of X̄ is given below:
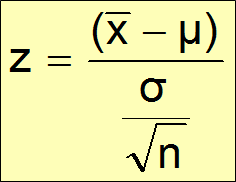
where:
- X̄sample mean
- μ = population mean
- σ = population standard deviation
- n = sample size
Example
Suppose a population has mean μ = 7 and standard deviation σ = 3.
Suppose a random sample of size n = 38 is selected.
Question: What is the probability that the sample mean is between 6.8 and 7.2?
Solution:
Even if the population is not normally distributed, the CLT can be used since the sample size, n, > 30
Hence, the sampling distribution of X̄ is approximately normal with mean μX̄ = 7, and
σX̄ = σ /
√ n
= 3 /
√ 38
= 0.4866
P(6.8 < μX̄ < 7.2) = P((6.8 − 7) / (3 /
√ 38
)) < ((μX̄ − μ / (σ / (
√ n
)) < ((7.2 - − 7 / (3 /
√ 38
))) = P(-0.41 < z < 0.41) = 0.31
For more details, please contact me here.