Introduction to Random Variables Using Statistics
Using Statistics
Consider the different possible orderings of boy (B) and girl (G) in three sequential births.
There are 2*2*2=23 = 8 possibilities, so the sample space is:
| BBB |
(3) |
GBB |
(2) |
| BBG |
(2) |
GBG |
(1) |
| BGB |
(2) |
GGB |
(1) |
| BGG |
(1) |
GGG |
(0) |
Note the following:
- each possible outcome is assigned a single numeric value
- all outcomes are assigned a numeric value, and
- the value assigned varies over all possible outcomes.
The count of the number of boys is hence a random variable:
A random variable, X, is a function that assigns a single, but variable, value to each element of a sample space.
See the illstration below:
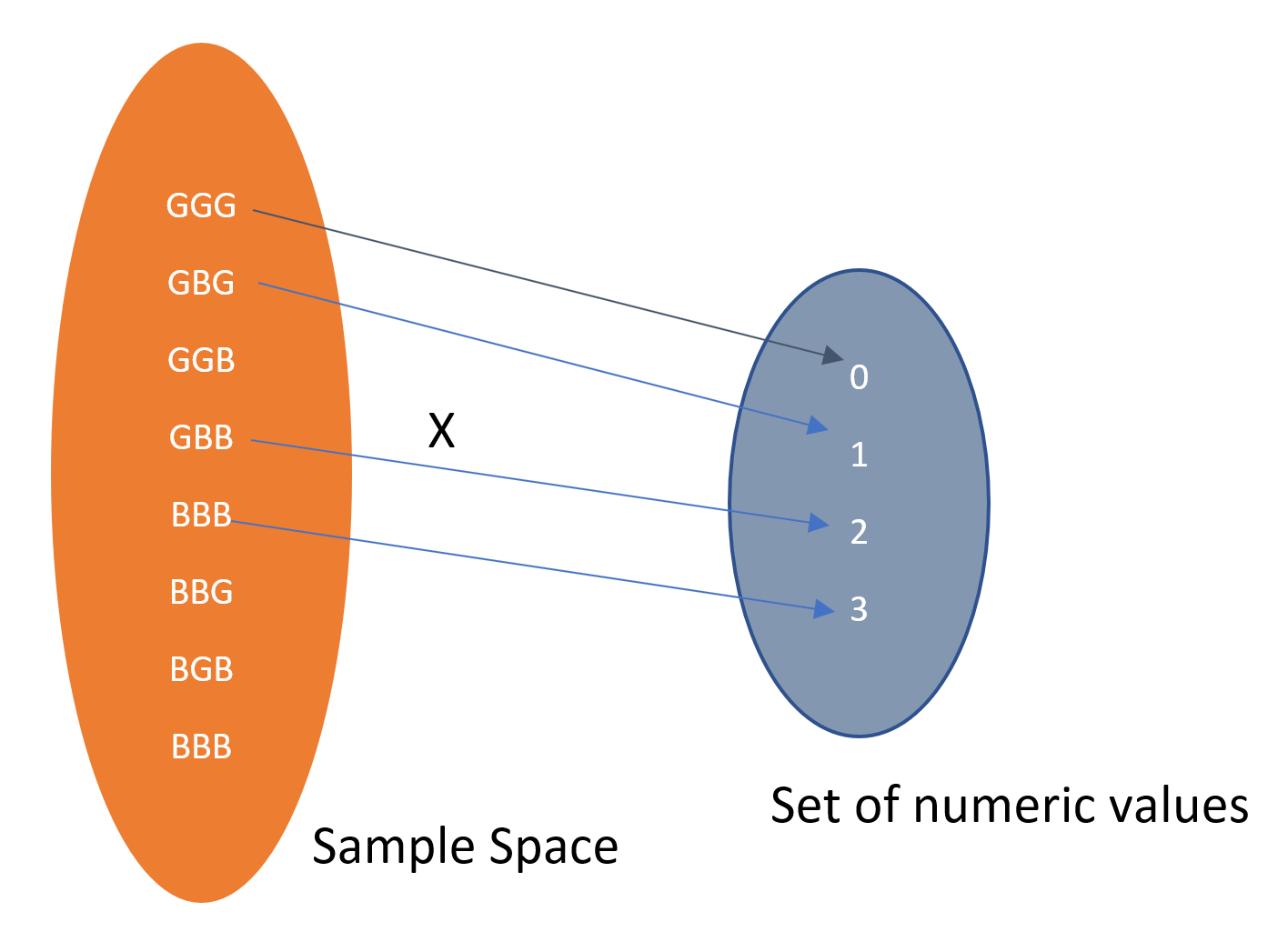
Since the random variable X = 2 when any of the three outcomes BBG, BGB, or GBB occurs,
P(X = 2) = P(BBG) + P(BGB) + P(GBB) = 3/8
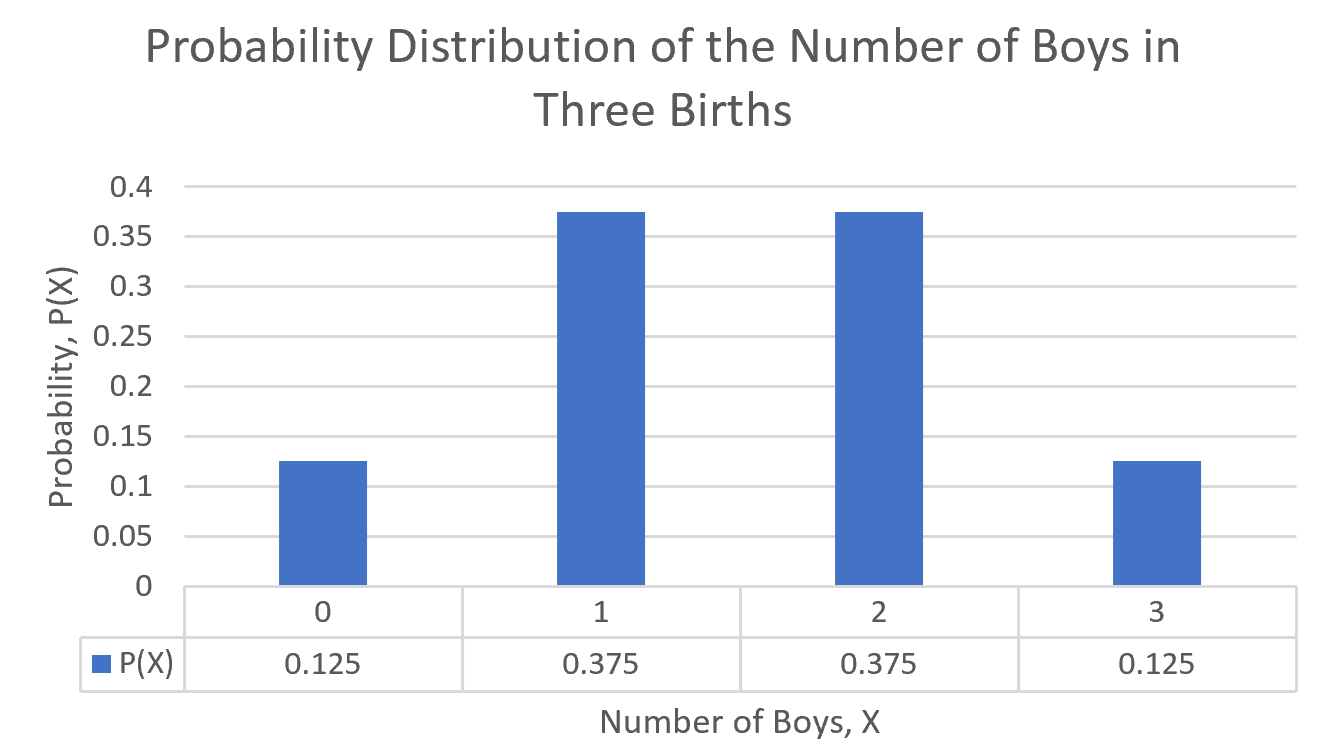
The probability distribution of a random variable is a table that lists the
possible values of the random variables and their associated probabilities.
| x |
P(x) |
| 0 |
1/8 |
| 1 |
3/8 |
| 2 |
3/8 |
| 3 |
1/8 |
|
Sum of P(x) = 8/8=1.0 |
The Graphical Display for this Probability Distribution is shown below:
Examples
Example 1
Consider the experiment of tossing two six-sided dice. There are 36 possible outcomes as illustrated below:
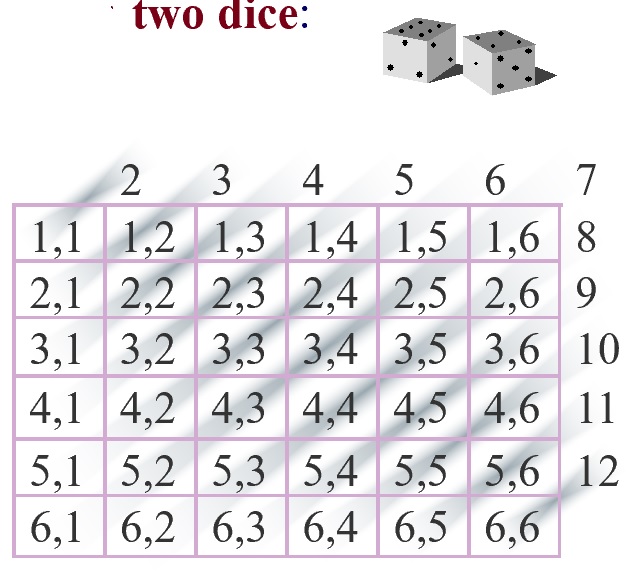
Let the random variable X represent the sum of the numbers on the two dice:
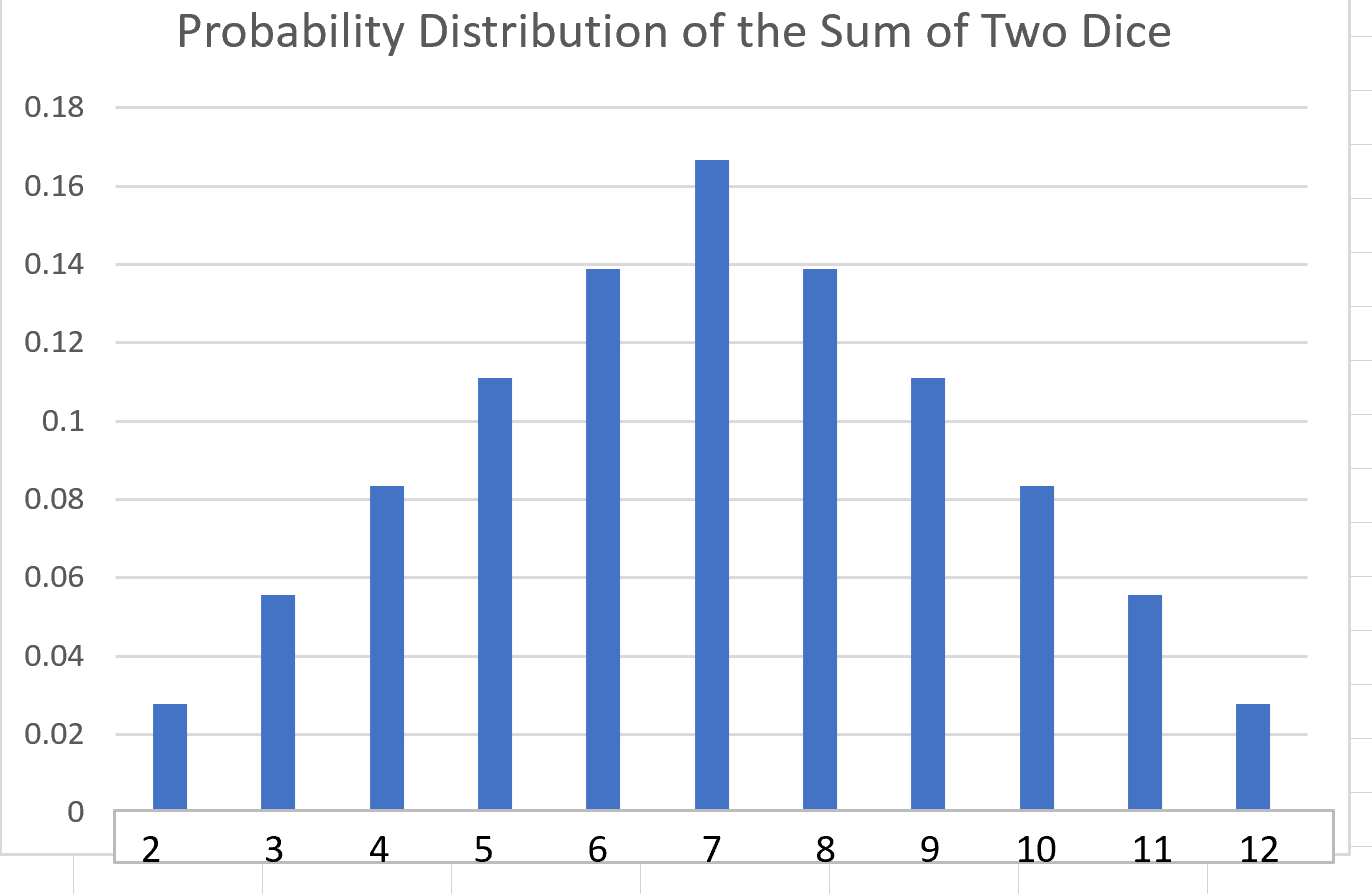
| x |
P(x) |
| 2 |
1/36 |
| 3 |
2/36 |
| 4 |
3/36 |
| 5 |
4/36 |
| 6 |
5/36 |
| 7 |
6/36> |
| 8 |
5/36> |
| 9 |
4/36 |
| 10 |
3/36 |
| 11 |
2/36 |
| 12 |
1/36 |
|
Sum of P(x)= 1.0 |
The probability distribution of the sum of the two dice is shown in the graph below:
Example 2
Probability Distribution of the Number of Switches:
A switch occurs when tossing a coin many times and then count how many times you get a Head (H) followed by a Tail (H) or
a Trail followed by a Head. For example in TTHHTHTTTH, there are 5 switches in total.
Consider the following an example of probability distribution of the number of switches:
| x |
P(x) |
| 0 |
0.2 |
| 1 |
0.1 |
| 2 |
0.2 |
| 3 |
0.1 |
| 4 |
0.3 |
| 5 |
0.1 |
|
Sum of P(x) = 1.0 |
The probability distribution of the sum of the two dice is shown in the graph below:
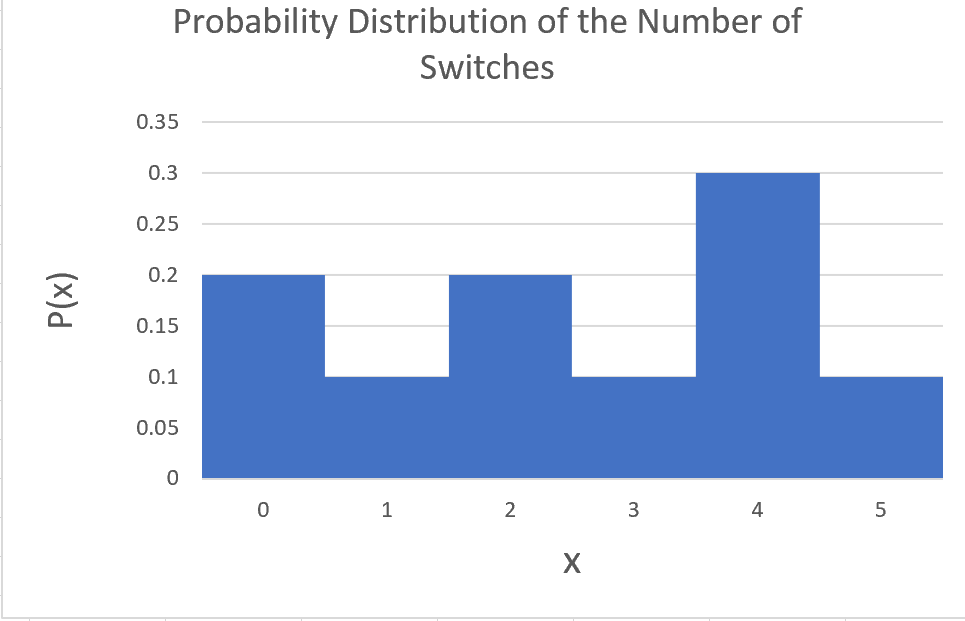
Probability of more than 2 switches P(X > 2) = P(3) + P(4) + P(5) = 0.2 + 0.1 + 0.1 = 0.4
Probability of at least 1 switch P(X ≥ 1) = 1 - P(0) = 1 - 0.1 = .9
For more details, please contact me here.




