Newton's Second Law
Defintion
The acceleration 'a' of an object in the direction of a resultant force F,
is directly proportional to the magnitude of the imposed force and
inversely proportional to the mass m of the object.
See below illustration regarding the two scenarios when the forces are unbalanced:
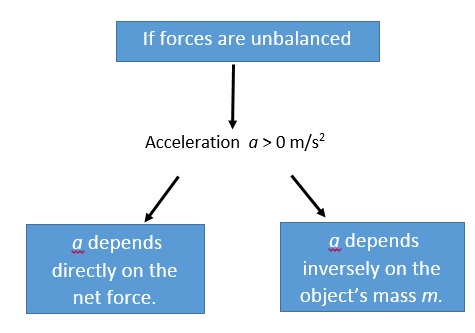
Newton’s second law is about the relationship between: force, mass, and acceleration.
1 Newton 1 kg • m/s2
Question: What happens when a force F acts on a mass m?
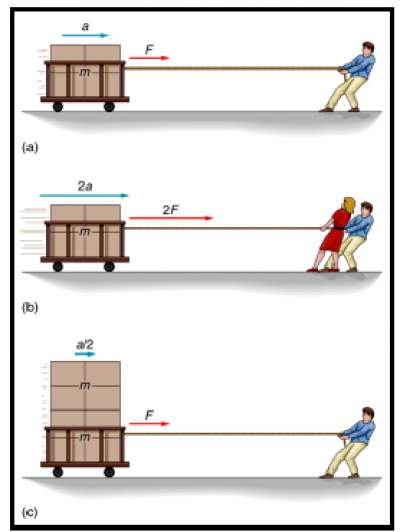
- (a) The force F produces an acceleration a.
- (b) If the mass m remains the same and the force F is doubled, the acceleration a is doubled.
- (c) If the mass m is doubled and the force F remains the same, the acceleration a is reduced by one-half.
Such relation can be expressed by the following formula:
Acceleration a = net force / mass = Fnet / m
Basically,
- When F increases, a increases as well (if F doubles, a doubles)
- When m increases, a decreases as well (if m doubles, a halves)
Example
Question: Calculate the acceleration of a 3000-kg, single-engine airplane as it begins its takeoff with an engine thrust of 1000 N.
Solution:
a = Fnet / m = 1000 / 3000 = 0.33 m/s2
Exercise
Based on the given table; Find the corresponding acceleration.
Check your answers here:
Solution
Example: Net force and the object's acceleration
If there is more than one vector acting on an object, the forces are added together as vectors,
taking into account their directions. See example below:
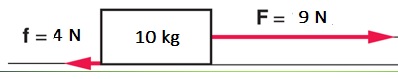
Fto the right = 9 N
Fto the left = 4 N
Fnet = 9 N - 4 N = 5 N (to the right)
a = Fnet / m = 5 N / 10 kg = 0.5 m/s2 (to the right)
Forces acting in opposite directions
As per the below figure, let's calculate the mass m of the box if its acceleration a is 5 m/s2
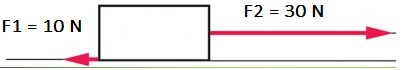
Solution:
The net force is 30 N - 10 N = 20 N, directed to the right.
Using the formula F = m×a, the mass m = F/a = (20 N)/(5 m/s2) = 4 kg.
Exercise
Click here to access a similar exercise.
Check your answers here:
Solution
Mass, Weight, and Inertia
- A bigger force is required to produce the same acceleration for the bigger mass.
- Inertia is known to be the object’s resistance to a change in its motion.
- Mass is a measure of an object’s inertia.
- The unit of mass is kilograms (kg).
- An object’s weight is the gravitational force acting on the object.
- Weight is a force, measured in newtons (N).
- In the absence of gravity, an object has no weight but having the same mass.
Example:
Assume a ball hangs from a string attached to the ceiling as per the illustration below:
Question: What would be the net force acting on the ball?
- The net force is upward
- The net force is zero
- The net force is downward
Answer: The net force is zero.
Explanation: Since the ball is hanging from the ceiling at rest, it is not accelerating hence the net force becomes zero.
There are two following forces acting on the ball canceling each other: Tension from the string and force due to gravitation:
For more details, please contact me here.
Date of last modification: 2024




