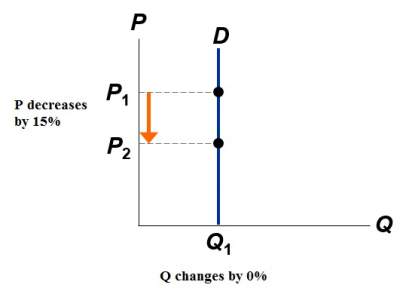
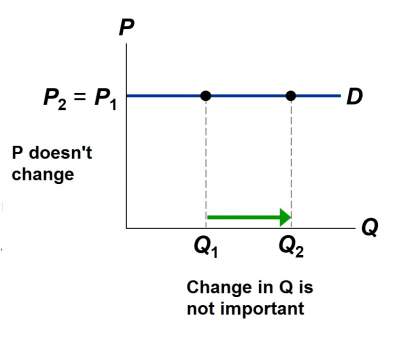
| D curve: Vertical |
| Consumers' price sensitivity: None |
| Elasticity: 0 |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
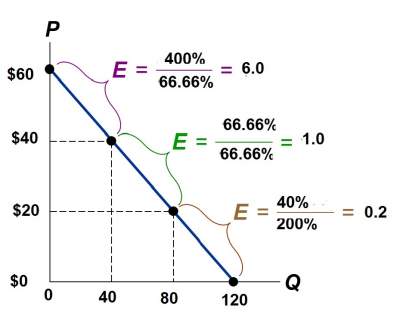
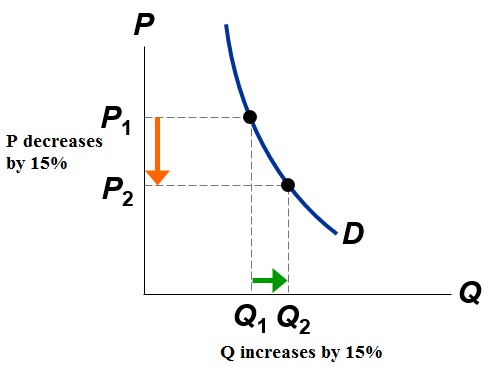
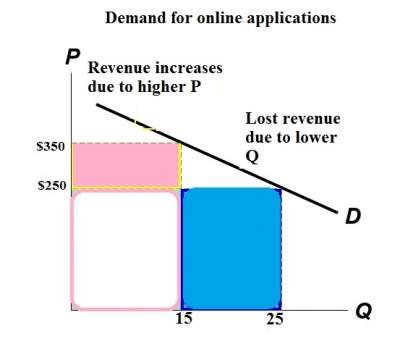
| Elastic demand. In this case, elasticity = 1.5 If P = $250, Q = 25 and revenue = $6250 If P = $350, Q = 15 and revenue = $5250 When D is elastic, a price increase causes revenue to fall. |
 |
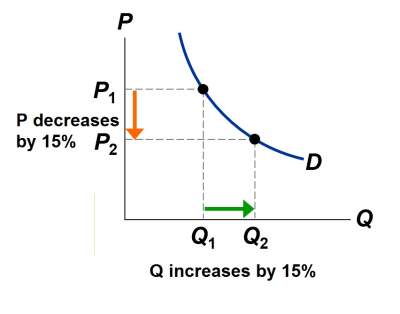
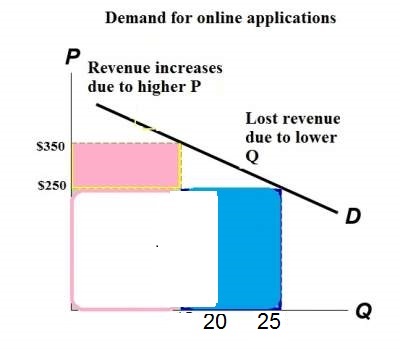
| Elastic demand. In this case, elasticity = 0.67 If P = $250, Q = 25 and revenue = $5000 If P = $350, Q = 20 and revenue = $7000 When D is inelastic, a price increase causes revenue to rise. |
 |