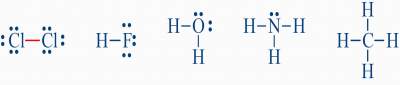Covalent Bonding
Introduction
- Results from sharing of electrons between two atoms.
- It mainly exists among non-metallic elements.
Example:
The Octet Rule:
" Atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons until they are surrounded by 8 valence electrons".
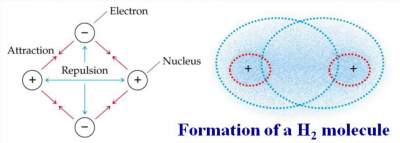
H· + H· → 

- These are called: "Lewis Structures" or "Lewis electron dot structures"
- In both structures, a covalent bond is created by sharing electrons between the two atoms, so that both atoms satisfy the octet rule
- For H2 molecule, although each H atom is surrounded by 2 electrons only, each H atom satisfy the octet rule since each H atom in the molecule resembles the nearest noble gas: He
Remark:
The number of valence electrons determines the number of covalent bonds an element will form:
If one electron ONLY is shared between the two atoms → Single Bond
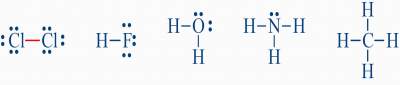
If more than one electron are shared between the two atoms, implying Multiple Bonds.

For more details, please contact me here.
Date of last modification: 2024