Bond Polarity and Electronegativity
Introduction
A Covalent Bond may be:
- Polar: when electrons in the bond are attracted to one of the atoms. Example: H-F bond
- Non-polar: when electrons are equally shared between atoms along the bond. Example: F-F bond
Polarity of the bond depends on the ability of one atom to attract the electrons of the bonds towards it more than the other atom → Electronegativity.
Electronegativity:
- he ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.
- The difference in electronegativity between the two elements sharing a covalent bond indicates its polarity .
- Hence, the trends of the "Electronegativity" in the Periodic TableThe "Electronegativity" scale.
Trends of the "Electronegativity" in the Periodic Table
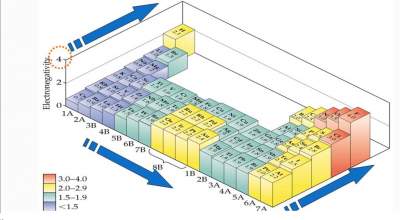
-
The highest electronegative element is F (4.0)
- The lowest electronegative element is Cs (0.7)
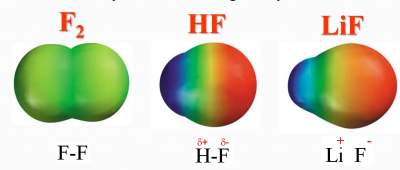
Examples
F2molecule (F-F)
- Difference is 4.0 − 4.0 = zero
- → Electrons are equally shared between the 2 F atoms
- → Non-polar covalent bond
HF molecule (H-F)
- Difference is 4.0 − 2.1 = 1.9
- → Electrons are more attracted towards F (higher electronegative)
- → Polar covalent bond
LiF molecule (Li-F)
- Difference is 4.0 − 1.0 = 3.0
- → Electrons are very attracted towards F
- → Ionic bond
Polarity of the bond is measured by the Dipole Moment (μ) = Q r
Where:
- μ = dipole moments
- Q = charge (in coulombs (c)
- r = distance between 2 charges (in m)
- The unit of μ called debye (D) where 1 D = 3.34 × 10− 30 coulomb-meter
Exercises on Bond Polarity and Electronegativity
Exercise I on Calculating the Dipole Moment (μ)
Check your answers here:
Solution to the Exercise I on Calculating the Dipole Moment (μ
Exercise II on Calculating the Dipole Moment (μ)
Check your answers here:
Solution to the Exercise II on Calculating the Dipole Moment (μ
Exercise III on Calculating the Dipole Moment (μ)
Check your answers here:
Solution to the Exercise III on Calculating the Dipole Moment (μ)
Relation between Bond Polarity & Bond Distance
Explanations:
- Bond electrons tend to be more on the bond as the difference in electronegativity between H and each of the halogens decreases.
- Size of the halogens increases as their atomic numberincreases; from top (F) to bottom (I)
For more details, please contact me here.
Date of last modification: Summer , 2019

