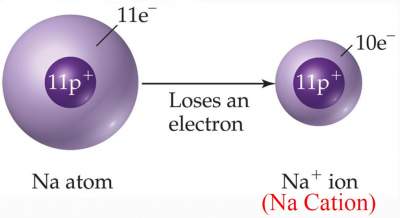
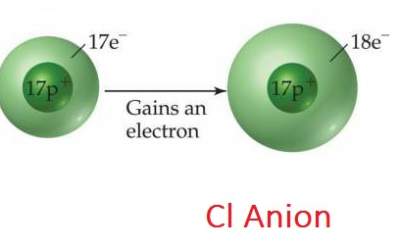
Atoms Combine to Form Molecules & Ion
Combine Atoms into Molecules & Ions
Molecule
It is an assembly of 2 or more atoms (of the sameor differentelement(s))tightly bound together,
and behave as a SINGLE unit with its own properties. Examples are shown below:
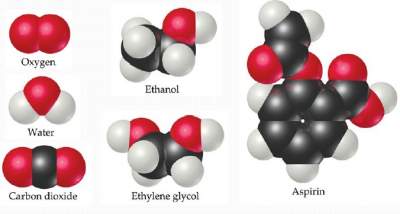
Note that most elements in the periodic table exist as SINGLE atoms but
there are a few that exist only in "diatomic" molecules,
such as: O2,H2, F2, Cl2, N2, Br2, and I2
Types of Molecules
- Molecular: Where two or more non-metallic atomes are bonded to each other
- Ionic: Where two or more metallic & non-metallic atoms are bonded to each other
Examples of Molecular: H2O, H2O2, HCl
Examples of Ionic: NaCl, FeO3, ZnS
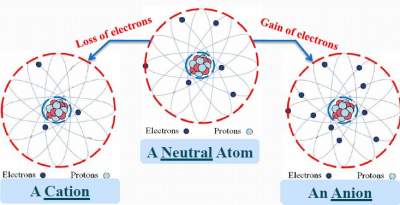
Ions and Ionic Compounds
Protons are entrapped inside an atom; their number CANNOT Change in a chemical reaction.
Only number of electrons can change during a chemical reaction. The loss and gain of electrons is illustrated below:
Examples
Ions and Ionic Compounds: Rules
- Metals tend to lose electrons forming Cations
- Non-metals tend to gain electrons forming Anions
- Ions such as Na+ and Cl− are called "Mono atomic ions"
- "Poly atomic ions" are atoms joined in a form of molecule, but with a positive or negative net charge.
Example: NO3− , SO42−
- Chemical properties of ions are totally different from their corresponding atoms because of the difference in charge.
Example: Na+ & Cl− ions are different from Na, Cl atoms.
Example
Assume you need to find out the number of protons and electrons that Se2− ion possess.
According to the periodic table, Se is an element with an atomic number of 34, which means # protons = 34.
Since charge = (# protons) − (# electrons), hence , -2 = 34 –(# electrons), which means (# electrons) = 36.
Exercise: Chemical Symbol and Atomic Mass
Exercise on Chemical Symbol and Atomic Mass
Check your answers here:
Solutions to the Exercise on Chemical Symbol and Atomic Mass
Predicting ionic charge
Atoms lose or gain electrons in order to reach the same number of electrons of the closest "Noble Gas".
Example 1
Na has an atomic number of 11. It tends to lose an electron (forming Na+) with 10 electrons = atomic number of Ne (The closest inert gas).
Example 2
Cl has an atomic number of 17. It tends to gain an electron (forming Cl− ) with 18 electrons = atomic number of Ar (The closest inert gas).
Example 3
Ba has an atomic number of 56. It tends to lose two electrons (forming Ba 2+) with 54 electrons = atomic number of Xe (The closest inert gas).
Formation of an Ionic Compound
Electrons lost by atoms to form cations are gained by other atoms to form anions in the same ionic compound.
Ionic Compounds Are NEUTRAL.
Example 1
Na+ & Cl− → NaCl
Mg2+ & 2Cl− → MgCl2
Example 2
If the positive charge on ion A ≠ negative charge on ion B. For example: Mg2+ and N3−
In this case the following rule applies:
Number of Mg ions = Charge on N ions AND Number of N ions = Charge on Mg ions
3 × Mg2+ = 6+ charges and 2 × N3− = 6 − charges ⇔ Mg3N2 has ZERO net charge.
Exercise: Formation of an Ionic Compound
Exercise on Formation of an Ionic Compounds & Empirical Formula
Check your answers here:
Solutions to the Exercise on Formation of an Ionic Compounds & Empirical Formula
Exercise: Formation of Ionic Compounds vs. Molecular Compounds
Exercise on Formation of Ionic Compounds vs. Molecular Compounds
Check your answers here:
Solutions to the Exercise on Formation of Ionic Compounds vs. Molecular Compounds
For more details, please contact me here.
Date of last modification: Summer , 2019